Imagine an online commerce ecosystem where your AI agents independently search for the right flights, optimize spending, and secure the most competitive prices- all that while ensuring every financial interaction stays protected. Doesn’t it sound like a dream? Well, no more!
Agentic payments in commerce are rapidly evolving, bringing unprecedented speed, precision, and intelligence to everyday transactions.
Agentic commerce, or the thought of implementing AI agentic payments in commerce, might sound exciting to businesses. However, not everyone is familiar with this new era of payments that is not heavily dependent on manual resources.
Agentic AI in e-commerce payments is about building AI agents that can learn, adapt, and independently execute financial tasks with minimal human oversight. But the question is, how does it actually work, or how to build an AI agent that can autonomously negotiate, purchase, and pay?
This blog is a one-stop guide that answers all your queries associated with Agentic payments. From its definition, foundation elements, use cases, benefits, future trends, and challenges to the stepwise development of AI agents for commerce, it covers everything.
Let’s begin!
What is Agentic Commerce
Agentic commerce depicts a transformative shift from human-dependent interactions to agent-driven actions. The conventional way of e-commerce involves human users exploring product catalogues, adding the product/service to the cart, and making a payment.
Now, Agentic AI in payments totally changes this scenario by reducing the need for human-driven actions. The intelligent agents can autonomously find and add the product/service to the cart and make transactions on behalf of the user. While independently performing tasks and making decisions, the agents remain aligned with human intent.
Let’s move on to exploring some interesting statistics, stepwise working, and the key elements of intelligent commerce agents.
Also Explore: A Comprehensive Guide to Agentic Web
Interesting Industry-Wise Statistics of Agentic Payments
Accenture’s Future of Money survey reveals the following amazing statistics about Agentic AI transforming payments across various industries worldwide:
- The health and public service industry can majorly (83%) utilize Agentic AI in commerce to manage chargebacks.
- 83% of retail companies are willing to use Agentic commerce for automated vendor payments.
- 77% of telecom organizations are planning to use Agentic payments for in-app and IoT-device-triggered payments.
- 75% of travel companies find cross-border payments as the best use of Agentic payments in commerce.
- 85% of insurance firms want to use Agentic AI commerce to manage supply chain finance.
How Does Agentic Payments in Commerce Work
Agentic AI in payments follows a stepwise working process to ensure transparency, security, and accuracy in the tasks performed and transactions made. Here is how it works:
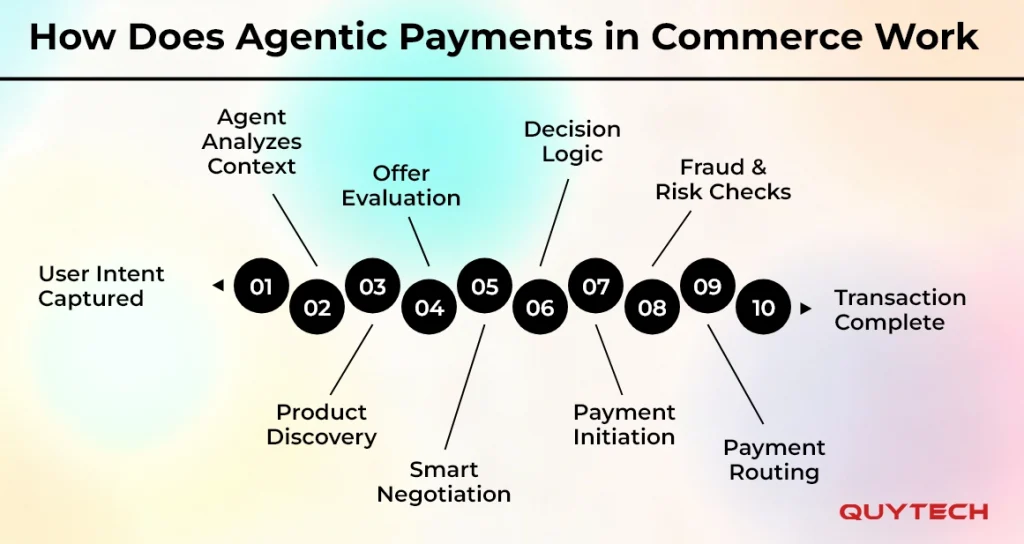
- User Intent Captured
In the first step, the user expresses an intent and enters inputs like “find and order the cheapest black t-shirt,” or “renew my home supplies.” What the intelligent commerce AI agent does is to understand what the user needs, their preferences, spending budget, and constraints.
- Agent Analyzes Context
The AI agent for commerce takes a look at the user’s previous purchases, behavior, inventory, pricing trends, and e-commerce merchant rules or instructions to comprehend everything before making a decision and completing the purchase.
- Product Discovery
Once it understands everything, the next step is to discover the product or service that the user needs. The AI commerce agent analyzes catalog data, marketplace listings, and other specifications to ensure the user gets what they want.
- Offer Evaluation
Agentic AI systems designed for autonomous transactions evaluate discount, loyalty points, and price to ensure grabbing the best offer to purchase the particular product or service that the user has requested.
- Smart Negotiation
The next step that an intelligent AI agent performs is to analyze the e-commerce merchant negotiation parameters or rules and consider the predefined strategies of the user to ask for a better price/discount, delivery, and other benefits.
- Decision Logic
In this step of Agentic payments in commerce working, the AI agent carefully analyzes all options and makes a decision considering the cost, speed, quality, and user preferences. They ensure the best offer is chosen for the user.
- Payment Initiation
The AI transaction agent looks into available payment methods and chooses the best one based on the success probability, security, and, of course, user preferences. In short, the step is about initiating the payment process.
- Fraud & Risk Checks
Before completing the payment process by entering required information, the agent analyzes transaction patterns, risk scores, and anomalies to make sure it is making a legitimate payment in a safe and secure space.
- Payment Routing
Agentic commerce agents thoroughly analyze routing paths across cards, A2A/UPI, wallets, and other payment options. The agent does this to choose the one with the highest reliability and lowest cost.
- Transaction Complete
Once everything is analyzed and the agent proceeds further by sending real-time notifications to users and completing the purchase with the selected payment method. Now, you saw that there was no manual intervention during the entire process.
You may like to read: The Impact of Agentic AI in Redefining Startup Growth
Key Elements of Agentic Commerce
Agentic commerce follows a layered approach focusing on intelligence, automation, and interoperability. They independently negotiate, purchase, and complete payments or transactions. Let’s understand the basic or foundational elements of Agentic commerce to learn how they do all this across consumer and enterprise environments.
Autonomous AI Agents
Intelligent agents that perform actions and make transactions on behalf of users or businesses. They can evaluate options, compare prices, verify policies, and autonomously make decisions and initiate transactions.
Multimodal Understanding & Real-Time Context Awareness
One of the core elements of Agentic AI in payments is that the agent understands text, voice, images, and structured as well as unstructured data. By analyzing this data, it comprehends user requests and purchasing conditions.
Negotiation & Decision-Making Engine
This engine is a core component that empowers AI agents to negotiate, purchase, and pay. It relies on reinforcement learning and utility-based models to evaluate tradeoffs and choose the best option.
Explore More: Agentic AI for Decision-Making: Embracing Autonomous Intelligence
Payment Intelligence Layer
The layer is a foundational element that manages payment initiation, authentication, routing, risk and fraud detection, and compliance adherence. It makes sure that the AI commerce agent can securely complete transactions using the best method.
Also Read: How AI is Transforming Fraud Detection in Digital Transactions
Merchant & Platform Integration APIs
Agentic commerce relies on standardized APIs and schemas to access product catalogs, get visibility into the inventory, check discounts and loyalty data, and more. These APIs enable the agent to interact seamlessly with any e-commerce platform.
Identity, Permissions, and Trust Framework
This component empowers intelligent commerce agents to verify identities and check permissions, budget, and approval workflows. Based on them, the agent ensures security and compliance of the transactions it makes.
Personalized and Preference Memory
It enables smart AI agents for transactions to store user preferences, including brand affinity, price thresholds, delivery expectations, and modes of payment. They can drive personalization in purchasing with this core element.
Interoperable Commerce Protocols
This element is responsible for seamlessly facilitating agent-to-agent communication. The protocols defined for the communication, along with standardized schemas, enable the agents across different platforms to collaborate and negotiate.
Compliance, Auditability, and Governance
This particular element gives businesses confidence that their agents are compliant and capable of securely making a decision and payment/transaction in agent-driven commerce. It also ensures their footprint is traceable and compliant.
Use Cases of AI Agentic Payments in Commerce
Agentic payments in commerce pave the way for high-efficiency and completely automated commerce experiences. It has multiple applications or use cases that are as follows:
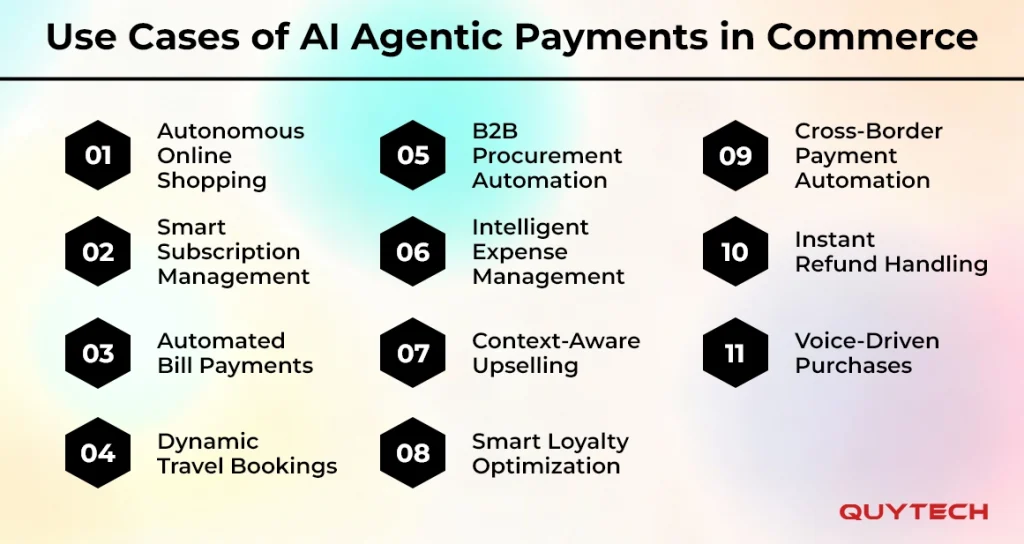
- Autonomous Online Shopping
Agentic AI in commerce is capable of monitoring business needs or a user’s specific requirements. When the supply runs low, they can even automatically order. Auto-replenishment of groceries, cleaning supplies, and pet food are some examples of AI agentic payments for users. Similarly, predictive B2B procurement for office or factory supplies is an example of Agentic AI payments in commerce for businesses.
Use Case Impact: It reduces manual effort and ensures fewer stock-outs and smarter replenishment.
Industries Benefited: Industries, including retail, e-commerce, FMCG, D2C, manufacturing, and other corporate offices, can make the most of this.
- Smart Subscription Management
Agentic payments in commerce can be used for smart subscription management by both users and businesses. Agents regularly monitor the usage of subscriptions, the date of renewal, and the preferences of a user or business. They can pause, upgrade, cancel, and even optimize subscriptions of OTT platforms, business services, SaaS tools, etc. This helps a business avoid overpayment or additional charges that may occur due to renewal after the plan expires.
Use Case Impact: Reduces churn, prevents overbilling, and ensures cost-optimized renewals.
Industries Benefited: SaaS, fitness & wellness, media/OTT, e-commerce, telecom.
- Automated Bill Payments
Automated bill payments are one of the best use cases of Agentic AI in commerce. Intelligent commerce agents keep an eye on due dates, previous payments, and other details to automatically schedule payments. They can even identify any unusual charges or negotiate to waive or reduce late fees. By choosing the best payment method, the agents can autonomously pay bills.
Use Case Impact: Prevents missed payments and improves financial accuracy.
Industries Benefited: Utilities, insurance, telecom, BFSI, enterprise operations.
- Dynamic Travel Bookings
Agentic commerce can also be used for travel bookings, where an AI agent books a travel based on users’ preferences, budget, loyalty programs, and other options. With continuous monitoring, the intelligent commerce agents grab the best deals on flights, accommodation, or business trips. These agents are even capable of adjusting bookings considering the weather, meeting changes, and other criteria.
Use Case Impact: Ensures cost-efficient travel booking with minimal human intervention.
Industries Benefited: Travel & hospitality, corporate travel, logistics, events.
- B2B Procurement Automation
Businesses spend a lot of time and a significant amount of money on ensuring inventory and procurement management. Agents can do the same by monitoring inventory, its usage pattern, vendor pricing, and supply schedules to source raw materials, office supplies, and renew equipment. Smart payment agents can even negotiate contracts, compare vendors, and place orders automatically while verifying that everything aligns with the company policies.
Use Case Impact: Lowers procurement costs, eliminates delays, and ensures consistent supply.
Industries Benefited: Manufacturing, retail, pharma, construction, and corporate offices.
- Intelligent Expense Management
Intelligent expense management is another significant use case of AI commerce agents. These intelligent assistants can review receipts, spending patterns of employees, and pre-defined corporate policies to classify expenses, approve compliant claims, and flag any anomalies. They can even initiate payments and reimbursements to speed up task execution without compromising accuracy.
Use Case Impact: Reduces processing time and minimizes compliance-related errors.
Industries Benefited: IT services, consulting, BFSI, and corporate finance teams.
- Context-Aware Upselling
Agentic payments done by smart agents can be used for context-aware upselling. In this, the agents carefully analyze customer behavior, real-time browsing patterns, cart context, and other aspects to autonomously opt-in for warranty extensions, personalized add-ons, and premium upgrades with the purchase.
Use Case Impact: Boosts average order value with highly relevant suggestions.
Industries Benefited: E-commerce, consumer electronics, automotive, and retail.
- Smart Loyalty Optimization
One of the amazing use cases of agentic payments in commerce is smart loyalty optimization. The agent automatically tracks loyalty points and their expiry dates, along with personalized merchant offers. Based on the expiration date, the agent can redeem points or merge reward programs to offer you maximized benefits.
Use Case Impact: Increases retention and ensures customers maximize their loyalty benefits.
Industries Benefited: Retail, airlines, hospitality, fintech, and travel.
- Cross-Border Payment Automation
Agentic commerce can be used for cross-border transaction automation. How? Well, intelligent commerce agents are capable of evaluating exchange rates, fees, settlement times, and regulations needed to conduct international transactions. They can even process payouts, invoice management, and global sales settlements with manual intervention.
Use Case Impact: Reduces transfer fees and ensures faster, compliant international payments.
Industries Benefited: Global e-commerce, exporters, marketplaces, IT outsourcing, and logistics.
- Instant Refund Handling
AI payments agents can efficiently and independently handle refunds. They can monitor return requests, check eligibility, and determine the fastest mode of refund. For this, it considers defined business rules. Agentic commerce can save a lot of time and effort that is required for refund management.
Use Case Impact: Improves customer satisfaction and speeds up post-purchase workflows.
Industries Benefited: E-commerce, D2C brands, retail, and ticketing platforms.
- Voice-Driven Purchases
Voice-driven purchases are another amazing application of Agentic AI in commerce. With this, consumers can provide voice inputs to an agentic AI system. The system understands the intent, browses for the product/services, automatically compares prices, and initiates a payment. It takes online shopping to the next level.
Use Case Impact: Reduces buying friction and increases convenience for hands-free commerce.
Industries Benefited: Smart home, retail, food delivery, automotive infotainment, and consumer electronics.
Read More: AI in Voice Commerce: Transforming Customer Experiences in Retail
Benefits of Agentic AI in Payments for Businesses and Consumers
Agentic AI commerce benefits both consumers and businesses. In other words, it is perfect for B2C and B2B; let’s understand how:
| Agentic Commerce Benefits for Businesses | Agentic Commerce Benefits for Consumers |
| Higher Conversion Through Zero-Friction Buying- It reduces cart abandonment, payment friction, and decision fatigue. | Hands-Off Convenience- It saves consumers from manual browsing, price comparisons, and re-entering payment information. |
| Access to High-Intent, Pre-Qualified Purchases- It shortens the sales cycle and boosts conversion. | Better Prices, Deals, and Value- Agentic AI commerce systems scan the market to enable consumers to get lower prices, automatic coupon application, best-value bundles, and negotiated discounts. |
| Dynamic Pricing & Negotiation Opportunities- It enables merchants to offer personalized pricing, provide real-time discounts based on inventory, trigger bulk or value-based deals, and promote bundles dynamically. | Smarter Budgeting & Spending Control- Agents consider preset budgets and enforce financial rules like monthly caps, category restrictions, and purchase approvals for higher-value items. |
| Reduced Operational Load- AI agents handling everything leads to fewer basic inquiries, lower ticket volumes, faster resolution cycles, and reduced service cost. | Personalized End-to-End Buying Journeys- Agents ensure personalized purchases by considering brand affinity, product quality thresholds, delivery priorities, and ethical or environmental considerations. |
| Better Forecasting & Inventory Optimization- Agents shared structured buying signals to enable merchants to forecast inventory more accurately, reduce overstock risks, align supply with predicted demand, and plan targeted promotions. | Stronger Security & Privacy- Enhances consumer trust as tokens and agent permissions ensure no raw credentials are stored, limited-scope risks, and reversible authorization. |
| Loyalty Optimization and Repeat Sales- Commerce agents provide more value if the merchant offers more discounts to boost lifetime value, basket size, and repeat purchase frequency. | Simplified Returns, Refunds & After-Sales- Agents manage all post-purchase tasks automatically to simplify returns and provide faster refunds. |
| Lower Fraud & Secure Transactions- The agent ensures authenticated transactions, lowers the risk of stolen cards, and reduces fraudulent chargebacks. | Financial Protection Through Intelligent Alerts- Agents alert consumers about early warnings for unusual transactions, prices drop on previously viewed items, and send notifications about subscription renewals or hidden charges. |
Technical Architecture of Agentic Payments in Commerce
When building an Agentic AI system for commerce, you have to have a thorough understanding of the technical architecture. To start with, agentic payments utilize a layered architecture where the agents can intelligently and seamlessly interact with merchant systems and payment mediums to facilitate autonomous transactions. Delve deeper to know more about these layers:
- User and Identity Layer
The layer is responsible for managing user authentication, biometrics, spending limits, and agent identity tokens to make sure every agentic payment is done securely and on behalf of the verified user only.
- AI Reasoning and Decision Layer
This layer brings intelligence by using LLMs, reasoning models, and policy engines. It makes the agent capable of understanding user goals, comparing prices, and making decisions related to purchase and payments.
- Commerce Integration Layer
The layer enables the agent to effortlessly connect to merchant APIs, product catalogs, inventory systems, and pricing engines. Agents can conduct real-time product searches, comparisons, and negotiations.
- Payment Infrastructure Layer
The payment infrastructure layer facilitates secure payment processing via tokenized payment credentials and orchestration engines. It also validates authentication flows and payment routing cards.
- Security, Risk, and Compliance Layer
This layer of the agentic payment in the commerce system offers encryption, anomaly detection, and fraud scoring. It is also responsible for verifying and complying with regulatory requirements and auditing logging.
- Communication and Protocol Layer
This layer utilizes standardized agent-to-merchant communication protocols to make sure every interaction is secured and well-structured.
Similar Read: AI Agents in E-Commerce: Everything You Need to Know
How to Implement AI Agentic Payments in Commerce
Follow this stepwise process to implement Agentic commerce in your business or build an AI agent for commerce or autonomous transactions:
Step 1: Agent Role and Scope Defining
The first step is to clearly define the tasks or roles an agent will perform. You can authorize the agent to search products, compare prices, negotiate, make payments, initiate refunds, and more. Also, define the spending limit and the approval or permission required in certain cases or scenarios.
Step 2: Create a Multimodal Intent Understanding Layer
As aforementioned, a multiple intent understanding layer enables a user to interpret user input in different forms. It makes the agent capable of translating broad user goals into actionable workflows.
Step 3: Connect to Merchant and Marketplace APIs
The next step is to integrate catalog APIs and other systems and engines to enable the intelligent commerce agent to seamlessly connect to merchants and discover products, make comparisons, and negotiate.
Step 4: Implement Negotiation and Decision-Making Models
Implement negotiation and decision-making models using reasoning models, reinforcement learning, and utility-based frameworks to empower agents to negotiate prices, delivery terms, and more.
Step 5: Build a Secure Payment Intelligence Layer
In this step, equip agents with a robust payment framework to enable commerce agents to tokenize credentials, score risks and check fraud, authenticate and authorize transactions, and choose payment modes.
Step 6: Integrate Identity, Permissions, and Delegation Controls
The next step is to create user identity verification, agent identity issuance, and other delegation tokens. This will make the intelligent assistant capable of making transactions on behalf of users.
Step 7: Adopt Agent-to-Merchant Commerce Protocols
Rely on emerging open standards, such as ACP, AP2, agent-commerce schemas, and others, to define how agents will interact with e-commerce platforms or merchants, exchange negotiation parameters, and finally, initiate transactions.
Step 8: Build Real-Time Monitoring and Auditability
Make sure you include dashboards, logs, and traceable decision trails. This would help you as a business to maintain transparency, meet regulatory requirements, and troubleshoot any behavior-related issues of the agents without any difficulty.
Step 9: Ensure Regulatory Compliance & Governance
Make sure the agentic commerce system that you design adherence to regulatory requirements and local payment-compliance controls. For this, include explainability layers and document everything, like how and why the agent made this decision.
Step 10: Deploy Continuous Learning and Optimization Systems
Build intelligent commerce agents that can automatically learn from outcomes. Whether it is a failed payment or a successful negotiation, they should be able to learn from their experience and improve their ability to deliver better outcomes.
Step 11: Test and Scale
Test the agentic payment flows by implementing various testing techniques in different scenarios. This will minimize operational risks. Once everything looks good, you can extend agent capabilities and hand over more responsibilities to it.
Compliance Requirements for Agentic Commerce
For the successful development of an Agentic AI system that facilitates automated digital transactions, it is essential to consider compliance requirements. Let’s take a look at these compliance requirements:
| Compliance | Description |
| Payment Compliance (PCI DSS, PSD2, RBI, Local Rules) | It ensures secure handling of payment data, strong customer authentication, tokenization, and adherence to regional payment regulations. |
| Data Privacy (GDPR, CCPA, DPDP Act) | This compliance is implemented for consent management, data minimization, purpose limitation, and user data rights for systems processing personal information. |
| AI Governance & Transparency (EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF) | The compliance mandates explainable AI, bias detection, continuous monitoring, and responsible model usage in autonomous decision-making. |
| Identity & Delegation Compliance | It takes care of identity verification, permission scopes, revocable access, and secure mandates that allow agents to act on behalf of users. |
| Fraud, AML & Risk Controls | With this compliance, businesses can ensure fraud detection, AML checks, anomaly scoring, and reporting protocols to secure automated financial transactions. |
Please note that the compliance requirements may vary depending on the region or country you are operating in. It is recommended to check the same before you build AI commerce agents or implement Agentic AI in payments.
Interesting Read: Agentic AI For Financial Advisors: Use Cases, Benefits, and More
5 Challenges in Agentic Payments and Ways to Overcome Them
Now that we have learned so much about AI agentic payments in commerce, it’s time to check out the challenges that you may encounter while implementing agentic commerce. Read below to know more about those challenges, along with the ways to address them:
- Data Privacy and Permission Control
For an AI agent to make a transaction, it requires access to sensitive data and transaction history. This may raise privacy concerns or lead to unauthorized actions.
To overcome this, implement granular-level permission settings and spend limits. Besides, use encrypted data vaults and invest in zero-trust frameworks.
- Security Risks and Fraud Vulnerability
Autonomous agents in commerce can be exploited due to weak identity, authentication, and authorization layers.
To address this challenge, you can enforce multi-factor and continuous authentication and integrate anomaly detection and real-time fraud models.
- Lack of Standardized Agent-to-Merchant Protocols
Different merchants and payment gateways utilize different APIs and schemas. For an AI agent, interacting with different platforms can lead to inconsistent interactions.
To address this challenge, make sure you adopt interoperable agent-commerce schemas. Also utilize LLM-aligned protocols and standardize atalog, pricing, and policy.
- Complex Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Agentic payments need to adhere to compliance and regulatory requirements, which can be difficult because of the different compliance requirements of each region and country.
To address this issue, you need to embed compliance-by-design and maintain agent activity logs. Also, utilize explainable AI, where the agent will be documented.
- Integration-Related Challenge
Legacy payment platforms, e-commerce backends, and ERP systems might not be compatible with autonomous agents.
To address this, you can ensure modular agentic middleware, use API-first architecture. Also, deploy agents as an extension of your existing systems.
Apart from the aforementioned ones, some other challenges with agentic commerce and agentic payments could be errors in decision-making, high operational and computational costs, and a lack of performance benchmarking.
Critical Insights: Revolutionizing Insurance Underwriting with Agentic AI
Top Companies Utilizing Agentic Payments
To understand the transformative potential of Agentic payments in commerce, let’s check the top companies that have already implemented them in their business:
VISA
The company is using an intelligent commerce system where AI agents can autonomously make transactions using credentialed access.
Mastercard
The world-renowned company has launched Agent Pay to ensure secure transactions and automated risk control.
PayPal
PayPal also uses an Agent Toolkit to enable AI agents to automatically access PayPal wallets and make payments.
Explore: How to Develop a Payment App Like PayPal? Comprehensive Guide to Develop
Future of AI Agentic Commerce
Before you build an AI agent that can autonomously make digital payments, take a look at what the future holds for Agentic commerce:
- In the upcoming times, we may witness the rise of fully autonomous shopping agents that can browse products, compare prices, negotiate, and buy.
- Multi-agent collaboration where customers, merchants, logistics, and payment agents can collaborate.
- Standardized agent-to-merchant protocols can be a promising future trend to facilitate safe delegation, credential sharing, and other use cases.
- Agent-driven personalization will shift static recommendations to dynamic and goal-based personalization that will be conducted by intelligent agents.
- In 2026 and the upcoming years, we may see powerful AI commerce agents expand into B2B and enterprise workflows.
- We may see a rise in AI commerce agents that can optimize themselves without manual intervention.
- Commerce with zero friction can become a future trend in Agentic payments.
Get Started with Quytech
Quytech is a leading Agentic AI development company with highly experienced and certified AI experts. With expertise in reasoning models, predictive analytics, secure payment integration, and enterprise-grade API engineering, our experts build agentic commerce systems that can buy, negotiate, and purchase autonomously.
We design end-to-end agentic architecture, which includes building agents that can understand intent, negotiate logic, and ensure tokenized payment workflows. These agents can be seamlessly integrated within your existing commerce stack, including catalogs, pricing engine, logistics networks, and payment systems.
The Agentic payment systems that we develop have compliance-ready frameworks aligned with PCI DSS, GDPR/CCPA, PSD2, DPDP, and emerging AI governance standards. You can build them for various use cases, including intelligent expense management, context-aware upselling, and subscription renewal management.
Final Words
Agentic payments in commerce enable a business to gain efficiency, higher conversion, and optimized revenue. It is a transformative shift in digital payments. AI agents can independently search, decide, negotiate, and complete transactions with unmatched efficiency. This also boosts conversion and gives a business a competitive advantage.
By choosing the right architecture and governance, and a reliable and experienced technology partner by your side, agentic commerce systems can be deployed safely and securely in your business.
FAQs
Implementing agentic payments in different businesses requires different capabilities. Some common ones include having basic API connectivity, a structured product catalog, a secure payment infrastructure, and clear governance policies.
This may vary depending on the nature and size of your business, the complexity of the project, the capabilities that you need in an agent, and a few other factors. Share your project requirements with Quytech’s experts for an accurate estimate.
No, Agentic payments can fit well within your current payment stack using orchestration layers and tokenized credentials. Businesses can upgrade components gradually without replacing core systems.
Incorrect decision-making, misapplied discounts, failed authentication, and unexpected spending behavior are some risks involved with agentic payment agents. Make sure you partner with an experienced Agentic AI development company that knows how to mitigate these risks.
Businesses can set various metrics, such as improvement in conversion rates, cart recovery, average order value, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and reduction in fraud or payment failures, as metrics to measure the ROI of the AI commerce agents.



